September 12, 2023
How to Choose Air Compressor Size
SHARE THIS POST

With so many options available, it can be a challenge to determine how to choose the best air compressor for your specific requirements. However, by understanding the factors and considerations involved, you can establish the size and type you need and make an informed decision that maximizes your productivity.
Once you know which size air compressor you need, you can ensure a reliable and efficient supply of compressed air for anything from inflating tires and operating pneumatic tools to powering industrial equipment and machinery.
What You Need to Know to Choose an Air Compressor
A properly-chosen air compressor will ensure you have the airflow you need to stay productive. To help you make the right call, review this guide to see how to calculate air demand, choose a design and power source, and decide what size air compressor you need to meet your requirements without overinvesting.
Determine Your Air Requirements
Learn how to calculate air demand by identifying the volume of air you need for your tools, measured in cubic feet per minute (cfm). You’ll need to measure the air pressure required for your intended applications as well, which is measured in pounds per square inch (psi). Understanding these fundamental parameters will be a solid foundation for your air compressor selection process.
Assess Your Applications
Next, carefully evaluate the applications that will draw from the air compressor. Different tasks demand varying amounts of compressed air. For instance, if you are involved in smaller projects that require minimal air usage, such as inflating tires or operating pneumatic tools intermittently, a smaller-sized air compressor may suffice. However, if you engage in more demanding applications such as sandblasting or running multiple tools simultaneously, a larger-sized compressor with higher cfm and psi ratings becomes imperative.
Consider Duty Cycle and Run Time
An air compressor’s duty cycle refers to how long it can operate within a given time frame. Consider the duty cycle when selecting an air compressor, as exceeding its recommended usage can lead to overheating and premature wear. Choosing a compressor with a high duty cycle and adequate cooling mechanisms is advisable if your tasks involve continuous or long-duration use. However, a compressor with a lower duty cycle may suffice for intermittent usage.
Evaluate Tank Size
The tank size of an air compressor determines its ability to store compressed air, which directly impacts its operation. A larger tank size is beneficial when using air tools that require large bursts of compressed air. However, a smaller tank size may be more suitable if portability is a primary concern or if you primarily engage in shorter tasks.
Consider Power Source
Air compressors have various power options, including electric- and gas-powered models. Electric compressors are typically more suitable for indoor applications due to their lower noise levels and emission-free operation. On the other hand, gas-powered compressors provide greater mobility and are ideal for outdoor or remote job sites where electricity may not be readily available.
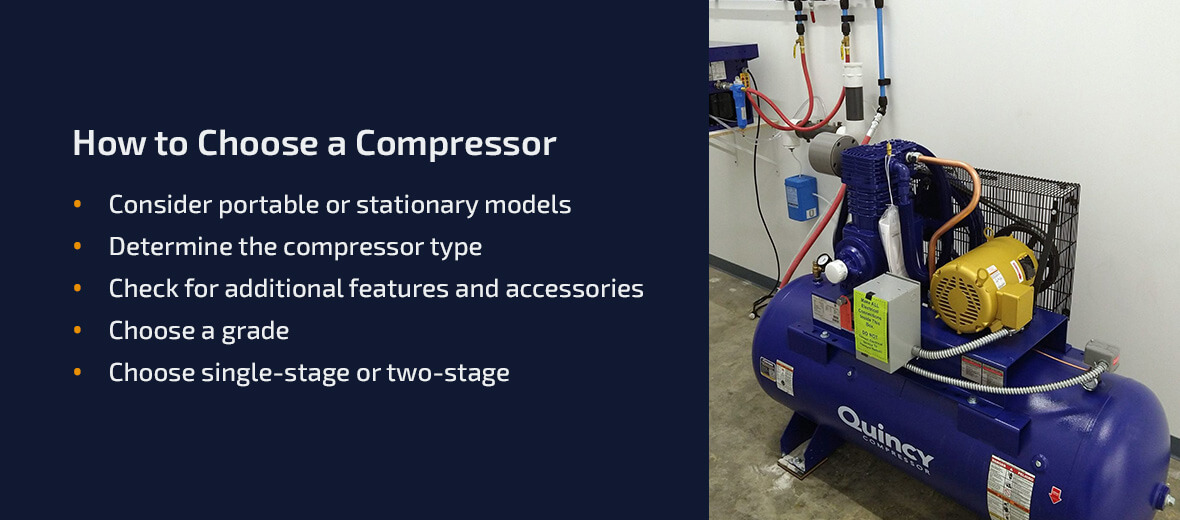
How to Choose a Compressor
Selecting the perfect air compressor can be daunting, considering the many available options. However, you can make a well-informed decision armed with the right knowledge and a clear understanding of your requirements:
- Consider portable or stationary models: Decide whether you require a mobile or stationary air compressor based on your working environment and mobility needs. Portable compressors are lightweight, compact and easy to move around, making them suitable for tasks that involve frequent location changes or remote job sites. On the other hand, stationary air compressors offer larger sizes for industrial work, making them ideal for fixed workspaces where mobility is not a priority.
- Determine the compressor type: There are three main air compressor types to choose from — reciprocating (piston), rotary screw and centrifugal compressors. Reciprocating compressors are commonly used for small- to medium-scale applications, offering affordability and versatility. Rotary screw compressors excel in continuous operation, providing high cfm outputs and efficient performance. Centrifugal compressors are suited for large industrial applications that demand high volumes of compressed air.
- Check for additional features and accessories: Look for additional features and accessories that can enhance the usability and efficiency of the air compressor. Some common features include adjustable pressure regulators, multiple outlets for simultaneous tool usage, built-in moisture separators and thermal overload protection.
- Choose a grade: Grades typically indicate the level of durability, performance and reliability of the compressor. Consumer-grade compressors are designed for occasional or light-duty use, making them suitable for DIY enthusiasts or small-scale projects. They offer affordability but are not made for continuous operation. Meanwhile, industrial compressors come in larger sizes and are engineered with high-quality components to withstand heavy use. Industrial-grade compressors are ideal for commercial applications that demand consistent and reliable operation.
- Choose single-stage or two-stage: Another crucial decision in selecting an air compressor is whether to opt for a single-stage or two-stage design. A single-stage compressor compresses air in a single stroke, delivering it directly into the storage tank. These compressors are suitable for lower-pressure applications and offer simplicity, affordability and compactness. Two-stage compressors initially capture air at a lower pressure, then pass it through a second cylinder for further compression, yielding higher overall efficiency, increased output and the ability to maintain higher pressures.
Air Compressor Types
Different compressor types offer unique advantages and are designed for various applications. Here, we explore four common types — rotary screw, reciprocating, centrifugal and oil-free compressors, to help you make an informed decision.
Rotary Screw Compressors
Rotary screw compressors work by trapping air between two rotating helical screws and compressing it as the screws mesh together. They deliver a steady supply of compressed air and are known for their high cfm output, making them ideal for demanding applications. Rotary screw compressors are relatively quiet, low-maintenance and capable of providing a constant flow of compressed air, making them suitable for continuous use in manufacturing, automotive and construction industries.
Reciprocating Compressors
Reciprocating compressors, also known as piston compressors, can be single-stage or two-stage and often find their utility in less demanding applications. These compressors rely on one or more pistons to compress air within a cylinder. Notable features of reciprocating compressors include their affordability, compactness and a flexible range of pressure settings. They are suitable for a wide array of applications, including automotive repair, woodworking and small-scale industrial jobs.
Centrifugal Compressors
Centrifugal compressors are ideal for high-volume, large-scale industrial applications demanding a substantial compressed air supply. Widely employed in power generation, oil and gas, and chemical industries, centrifugal compressors are renowned for delivering exceptionally high cfm outputs while efficiently handling large volumes of air. With their reputation for reliability and low maintenance requirements, centrifugal compressors are frequently found in continuous-operation scenarios in large industrial facilities.
Oil-Free Compressors
Oil-free compressors are meticulously engineered to deliver compressed air that is uncontaminated and devoid of any traces of oil. By ensuring the compressed air is completely free from oil particles, these compressors guarantee a safe and clean air supply, thereby minimizing the risks associated with contamination and the potential damage to delicate equipment.
These compressors eliminate the need for lubricating oil by integrating innovative design features such as advanced filtration systems and no-contact parts. In applications where oil contamination poses a concern, such as food and beverage processing, pharmaceuticals, electronics manufacturing and painting, oil-free compressors are vital pieces of equipment.
Order Your New Compressor From C.H. Reed, Inc.
If you’re unsure what type or size air compressor you need, a professional with the Compressed Air Group at C.H. Reed is ready to help. We understand the importance of equipment reliability and have the expertise and products to help companies like yours achieve optimal performance. Our team provides a wide range of sustainable solutions tailored to all air compressor sizes, plus valuable experience and a comprehensive portfolio of products and services to support your operations.
Contact C.H. Reed today and discover how our range of sustainable solutions can enhance your compressed air system, drive productivity and deliver tangible results for your business.
Search
Categories
Get a consultation
Related Posts
The 3 Distinct Advantages of Hydraulic Powered Pumps
Recently, C. H. Reed helped a major printing operation install a new ink pumping system. The new system needed to transfer four colors of high viscosity, heat-set ink to their three presses, drawing the ink from multiple 5,000…
Simple Ways to Reduce Waste in Your Spray Finishing System
In today’s demanding manufacturing landscape, it can be convenient to adopt a “cut-costs-at-all-costs” mentality, justifying questionable means for the sake of leaner production, a lower bottom line and increased profitability. Regrettably, those efforts can interfere…
What You Need to Know About Air-Powered Pressure Washers
Pressure washers are great solutions for your average cleaning applications, but what tool do you turn to for your more challenging applications? There are many instances where it is simply impossible to use a traditional…
